Christmas Music
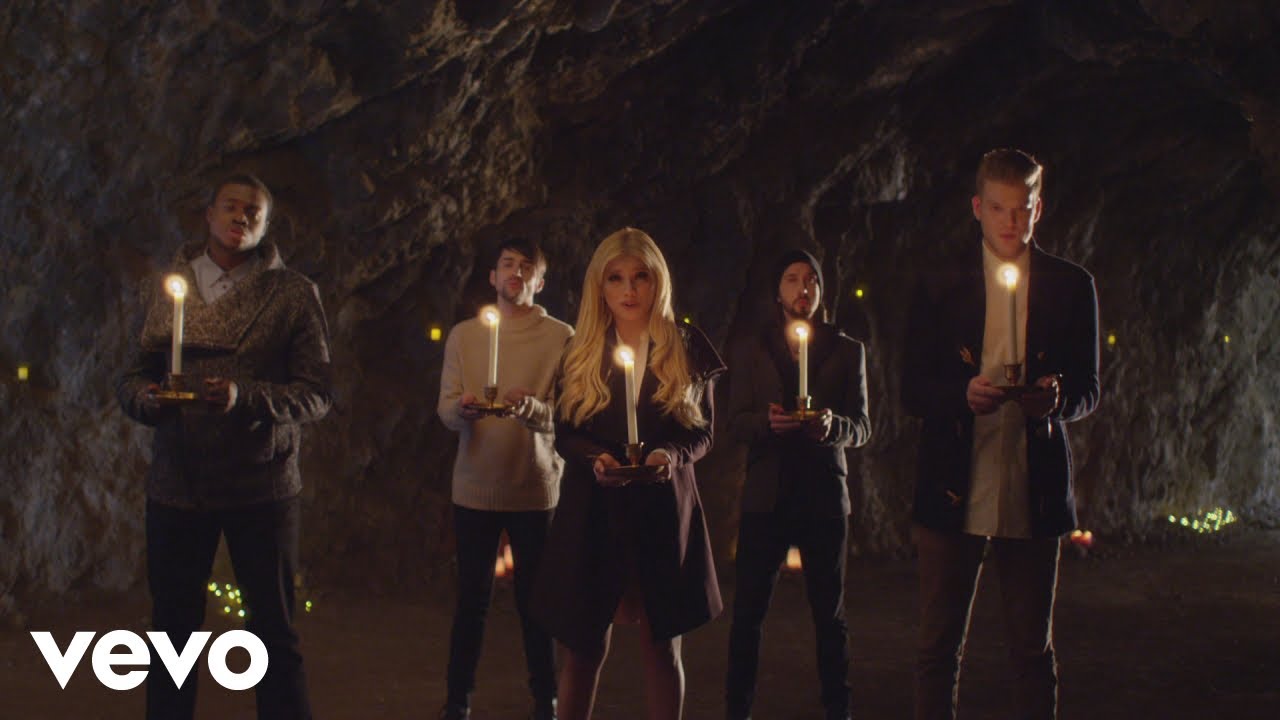
The first recording is the classic, ‘Mary did you know’, by one of my favourite groups – Pentatonix. “Mary, Did You Know?” is a Christmas song addressing Mary, mother of Jesus, with lyrics written by Mark Lowry in 1984, and music written by Buddy Greene in 1991. It was originally recorded by Christian recording artist Michael English on his self-titled debut solo album in 1991. At the time, English and Lowry were members of the Gaither Vocal Band, and Greene was touring with them. The song reached Number 6 on CCM Magazine’s Adult Contemporary Chart.[2] Lowry would record the song several times himself, most notably with the Gaither Vocal Band on their 1998 Christmas album, Still the Greatest Story Ever Told.
The song has since gone on to become a modern Christmas classic, recorded by hundreds of artists over the years, across multiple genres. Several recordings have reached the top ten in the Billboard R&B and Holiday charts. The song encourages contemplation of the relationship between Mary and her son, although some religious commentators have criticized the lyrics for downplaying Mary’s own grace and understanding.
The second recording is the London Symphony Orchestra performing well know Christmas Carols/songs. The London Symphony Orchestra (LSO) is a British symphony orchestra based in London. Founded in 1904, the LSO is the oldest of London’s symphony orchestras. The LSO was set up by a group of players who left Henry Wood’s Queen’s Hall Orchestra because of a new rule requiring players to give the orchestra their exclusive services. The LSO itself later introduced a similar rule for its members. From the outset the LSO was organised on co-operative lines, with all players sharing the profits at the end of each season. This practice continued for the orchestra’s first four decades.
The LSO underwent periods of eclipse in the 1930s and 1950s when it was regarded as inferior in quality to new London orchestras, to which it lost players and bookings: the BBC Symphony Orchestra and the London Philharmonic Orchestra in the 1930s and the Philharmonia and Royal Philharmonic after the Second World War. The profit-sharing principle was abandoned in the post-war era as a condition of receiving public subsidy for the first time. In the 1950s the orchestra debated whether to concentrate on film work at the expense of symphony concerts; many senior players left when the majority of players rejected the idea. By the 1960s the LSO had recovered its leading position, which it has retained subsequently. In 1966, to perform alongside it in choral works, the orchestra established the LSO Chorus, originally a mix of professional and amateur singers, later a wholly amateur ensemble.
As a self-governing body, the orchestra selects the conductors with whom it works. At some stages in its history, it has dispensed with a principal conductor and worked only with guests. Among conductors with whom it is most associated are, in its early days, Hans Richter, Sir Edward Elgar, and Sir Thomas Beecham, and in more recent decades Pierre Monteux, André Previn, Claudio Abbado, Sir Colin Davis, and Valery Gergiev.
Since 1982, the LSO has been based in the Barbican Centre in the City of London. Among its programmes there have been large-scale festivals celebrating composers as diverse as Berlioz, Mahler and Bernstein. The LSO claims to be the world’s most recorded orchestra; it has made gramophone recordings since 1912 and has played on more than 200 soundtrack recordings for the cinema, of which the best known include the Star Wars series. The LSO is consistently ranked as one of the world’s leading orchestras.
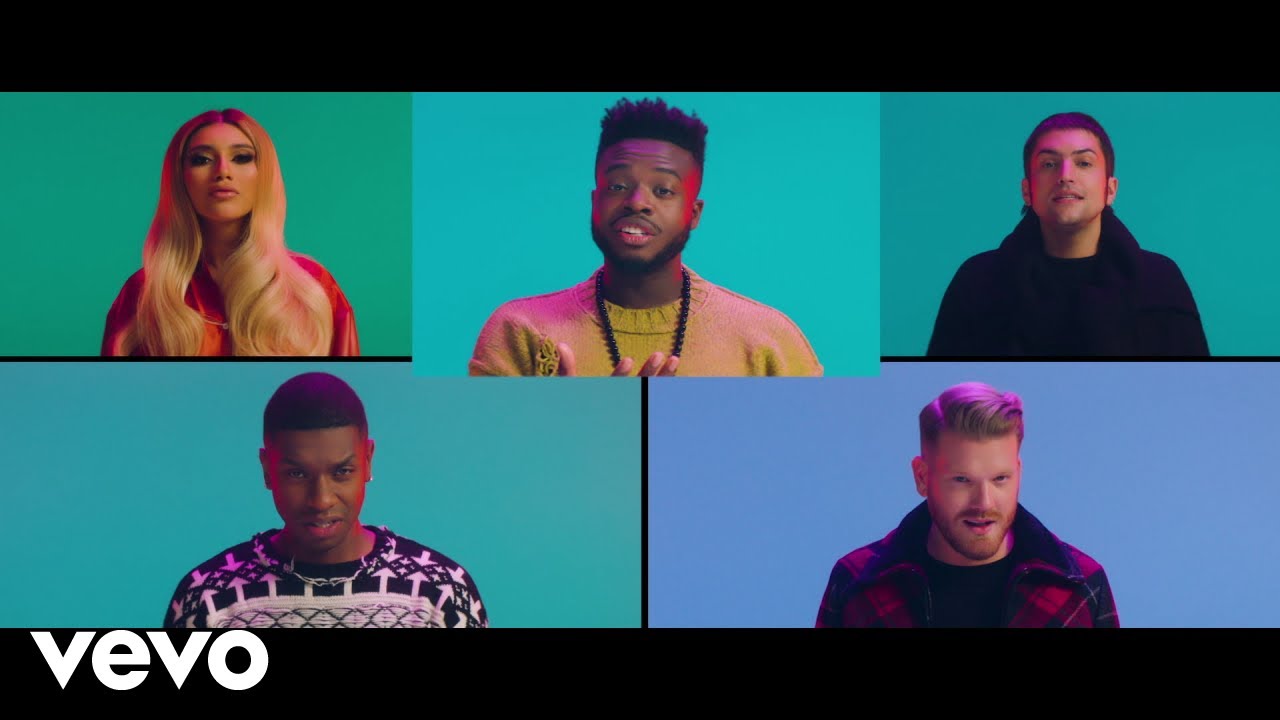
The Third recording is Pentatonix once again with ‘The Twelve Days of Christmas’: “The Twelve Days of Christmas” is an English Christmas carol that enumerates in the manner of a cumulative song a series of increasingly numerous gifts given on each of the twelve days of Christmas (the twelve days that make up the Christmas season, starting with Christmas Day). The song, published in England in 1780 without music as a chant or rhyme, is thought to be French in origin. “The Twelve Days of Christmas” has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 68. The tunes of collected versions vary. The standard tune now associated with it is derived from a 1909 arrangement of a traditional folk melody by English composer Frederic Austin, who introduced the familiar prolongation of the verse “five gold rings” (now often “five golden rings”).
And lastly what would Christmas be without the music of the Nutcracker? The Nutcracker is an 1892 two-act ballet (“fairy ballet”), originally choreographed by Marius Petipa and Lev Ivanov with a score by Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky (Op. 71). The libretto is adapted from E. T. A. Hoffmann’s story “The Nutcracker and the Mouse King”.
Although the original production was not a success, the 20-minute suite that Tchaikovsky extracted from the ballet was. The complete Nutcracker has enjoyed enormous popularity since the late 1960s and is now performed by countless ballet companies, primarily during the Christmas season, especially in North America. Major American ballet companies generate around 40% of their annual ticket revenues from performances of The Nutcracker. The ballet’s score has been used in several film adaptations of Hoffmann’s story.
Tchaikovsky’s score has become one of his most famous compositions. Among other things, the score is noted for its use of the celesta, an instrument that the composer had already employed in his much lesser known symphonic ballad The Voyevoda.